
How to pass PENRE:
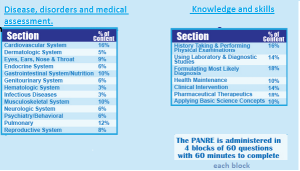
The Physician Assistant National Recertifying Examination, commonly known as the PANRE, is a comprehensive and challenging examination for men and women who hope to enter this exciting field of health care. The content of this exam is divided into the following seven task areas: history taking and performing physical examinations (16% of the exam), using laboratory and diagnostic studies (14%), formulating most likely diagnosis (18%), health maintenance (10%), clinical intervention (14%), pharmaceutical therapeutics (18%), and applying basic science concepts (10%). In the section on history taking and performing physical examinations, you must demonstrate knowledge of pertinent historical information, risk factors, signs, and symptoms. The following skills are covered in this task area of the PANRE: conducting interviews, identifying historical information, performing physical examinations, associating current complaint with presented history, and identifying physical examination information. In the section on using laboratory and diagnostic studies, you must demonstrate knowledge of indications, cost-effectiveness, relevance of common screening tests, normal and abnormal diagnostic ranges, risks, and appropriate patient education. The skills covered in this section of the PANRE include using diagnostic equipment, selecting specimens, and interpreting study results. In the section on formulating the most likely diagnosis, the following subjects are covered: significance of history, physical findings, and diagnostic and laboratory studies as they relate to diagnosis. The skills required for success in this section include correlating normal and abnormal diagnostic data, formulating differential diagnoses, and selecting the most likely diagnosis in light of presented data. In the health maintenance task area of the PANRE, the required knowledge includes epidemiology, early detection and prevention, relative value of common screening tests, appropriate patient education regarding preventable conditions or lifestyle modifications, and healthy lifestyles. The skills required for this section include using counseling and patient education techniques, communicating with patients, adapting health maintenance to the patient’s context, and using the informational database. Finally, the clinical intervention task area of the PANRE requires knowledge of the management and treatment of selected medical conditions and indications, contraindications, complications, risks, benefits, and techniques. The skills required for this section include formulating and implementing treatment plans, recognizing and initiating treatment for life-threatening emergencies, demonstrating technical expertise related to performing specific procedures, communicating effectively, facilitating patient adherence and active participation in treatment, and interacting effectively in multidisciplinary teams. The PANRE was developed by the National Commission on Certification of Physician Assistants.
Here are some informative videos..
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F2kDOfBn1S0
Time and marks devision are as following:

http://https//www.youtube.com/watch?v=ouJjPGu3JXY
Following are some practice questions
1. A 16-year-old Hispanic female presents to the clinic complaining of severe pain in her right ear. She is on the local high school swim team and has been participating in extra practice sessions. Her ear pain is so severe that she cannot lie on her right side to sleep. On physical exam, the right tragus is tender to palpation. The right ear canal is swollen and has scant white, clumpy discharge. Culture of this discharge would most likely reveal what organism?
A. Haemophilus influenzae
B. Moraxella catarrhalis
C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D. Streptococcus pneumoniae
2. A 72-year-old widowed woman presents to the office with the odor of alcohol on her breath on repeated office visits. When asked about alcohol use, she flatly denies it. Which of the following laboratory studies would best support a diagnosis of alcohol abuse in this patient?
A. elevated g-glutamyltransferase (GGTP)
B. elevated high-density lipoproteins (HDL)
C. microcytic anemia
D. reduced transaminase enzymes
3. A 22-year-old female complains of cold intolerance. She is 5 ft 4 in and weighs 95 lb. She has not had a normal menses in over a year. Skin is dry and scaly with increased lanugo. Which of the following laboratory abnormalities is most likely to be found in this patient?
A. elevated cholesterol
B. increased thyroxin (T4)
C. increased follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
D. sinus tachycardia on ECG
4. A 26-year-old female comes to the ER with complaints of white vaginal discharge and pelvic pain. She admits to having unprotected sex. On physical examination, she has an inflamed cervix and cervical motion tenderness. Which one of the following two-medication pairs should she receive prior to leaving the ER?
A.Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM and clindamycin 300 mg po
B.Clindamycin 300 mg po and azithromycin 1 gm po
C.Mefoxitin 2 gm IV and azithromycin 1 gm po
D.Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM and azithromycin 1 gm po
Answers
1. C: The majority of cases of otitis externa are caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Proteus spp. Less common causes include Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Aspergillus, and Actinomyces. Topical antibiotic coverage should include antipseudomonal activity
2.A: The GGTP is generally elevated in alcohol abuse and is one of the best early indicators of alcohol abuse.
3.A: Elevated cholesterol, liver enzymes, and BUN and creatinine are common in patients with anorexia nervosa.
4.D: Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM injection in a single dose plus azithromycin 1 gm PO in a single dose or doxycycline 100 mg PO BID for seven days is the recommended regimen for treating gonorrhea (GC)/chlamydia infections. Clindamycin and Maxipime are not given as treatment for either gonorrhea or chlamydia. The patient should be treated in the ER for suspected GC/chlamydia infection to prevent the patient from potentially spreading the disease.
Leave a Reply