Active Transport and Passive Transport Across A Cell Membrane
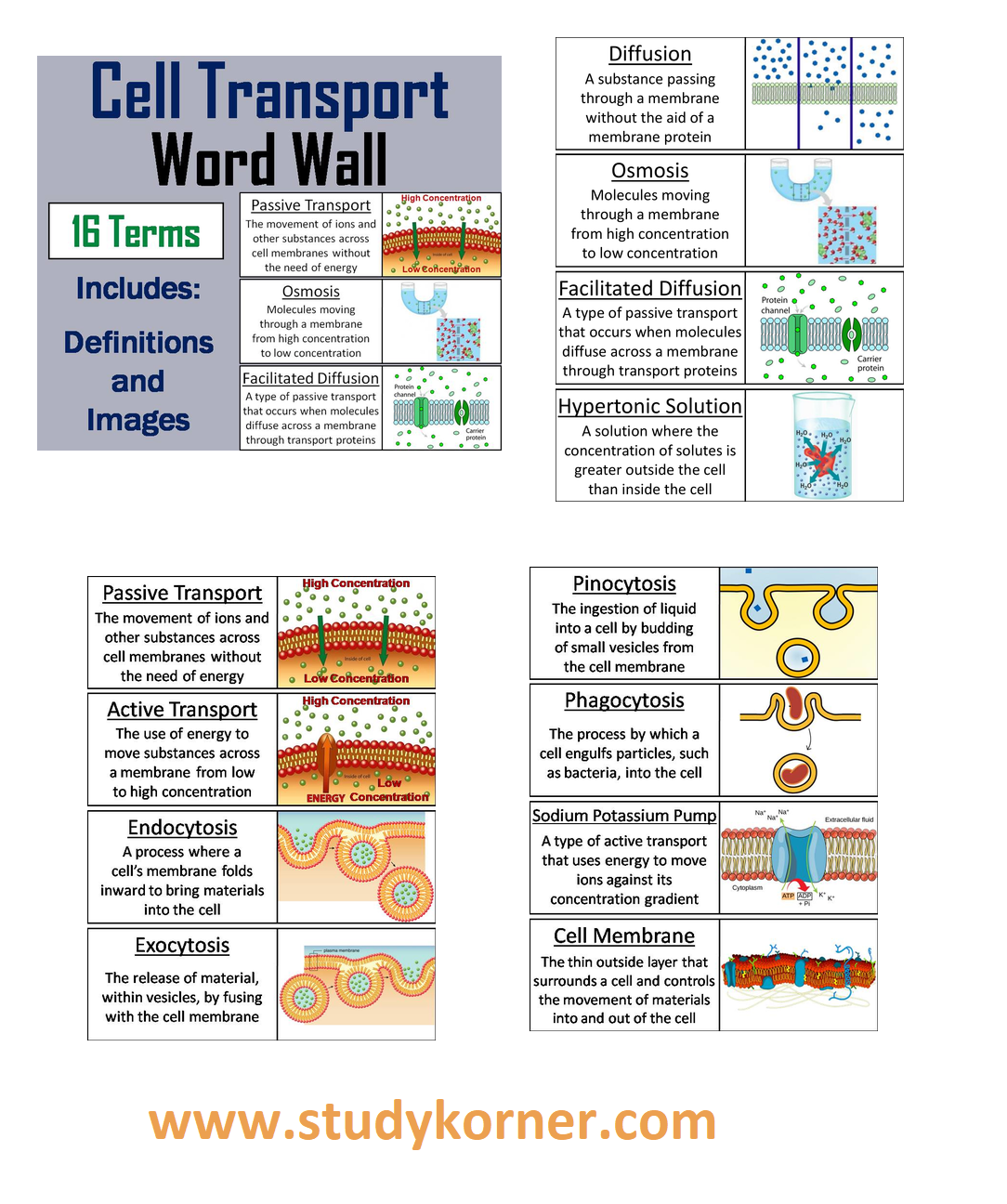
3 types of membrane transport
Basic types of membrane transport, simple passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion (by channels and carriers), and active transport.
♦ Active Transport
♦ Carrier Protein
♦ Cell Membrane
♦ Channel Protein
♦ Diffusion
♦ Endocytosis
♦ Exocytosis
♦ Facilitated Diffusion
♦ Hypertonic Solution
♦ Hypotonic Solution
♦ Isotonic Solution
♦ Osmosis
♦ Passive Transport
♦ Phagocytosis
♦ Pinocytosis
♦ Sodium Potassium Pump
Types of Active Transport
- Antiport Pumps. Active transport by antiport pumps
- Symport Pumps. Symport pumps take advantage of diffusion gradients to move substances
- Endocytosis
- Exocytosis
- Sodium Potassium Pump
- Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein
- White Blood Cells Destroying Pathogens
Types of passive transport
The rate of passive transport depends on the permeability of the cell membrane, which, in turn, depends on the organization and characteristics of the membrane lipids and proteins. The four main kinds of passive transport are simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, filtration, and/or osmosis.
| Transport | Molecules moved | Uses energy? | Example transporter/disease |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple diffusion | Small, nonpolar | No | Pulmonary edema |
| Facilitated diffusion | Polar molecules, larger ions | No | GLUT4 / Diabetes Mellitus Type II |
| Primary active transport | Molecules moving against their gradient coupled to the hydrolysis of ATP | Yes | Sodium-potassium pump, proton pump / atrial fibrillation, acid reflux |
| Secondary active transport | Molecule going with + molecule going against gradient | Yes | Sodium-calcium exchanger, SGLT2 |
Leave a Reply